力扣刷题
力扣刷题
基础知识
1 数据结构简介
- 线性数据结构
- 数组
- 链表:
- 栈:
LinkedListaddLast(E e)、removeLast()
- 队列:
Queueoffer(E e)、poll()
- 非线性数据结构
- 树
- 堆
- 散列表
- 图
2 stream 流处理
- 中间处理
filter()limit()
- 最终处理
forEach()count()collect()
1 | Arrays.stream(new int[]{...}).max().getAsInt(); // 获取int数组最大值 |
解题
一 链表
1 图书整理Ⅰ
书店店员有一张链表形式的书单,每个节点代表一本书,节点中的值表示书的编号。为更方便整理书架,店员需要将书单倒过来排列,就可以从最后一本书开始整理,逐一将书放回到书架上。请倒序返回这个书单链表。
2
3
输出:[1,4,6,3]
法1:计算长度,然后插入
法2:先正向遍历,插入栈中,然后一个一个出栈
法3:递归:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19class Solution {
int[] res;
int i = 0;
int j = 0;
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
solve(head);
return res;
}
public void solve(ListNode head){
if(head == null){
res = new int[i];
return;
}
i++;
solve(head.next);
res[j] = head.val;
j++;
}
}
2 反转链表
双指针
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12class Solution {
public ListNode trainningPlan(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode tmp = cur.next; // 暂存后继节点 cur.next
cur.next = pre; // 修改 next 引用指向
pre = cur; // pre 暂存 cur
cur = tmp; // cur 访问下一节点
}
return pre;
}
}递归
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11class Solution {
public ListNode trainningPlan(ListNode head) {
return recur(head, null); // 调用递归并返回
}
private ListNode recur(ListNode cur, ListNode pre) {
if (cur == null) return pre; // 终止条件
ListNode res = recur(cur.next, cur); // 递归后继节点
cur.next = pre; // 修改节点引用指向
return res; // 返回反转链表的头节点
}
}k个一组反转链表,不足k个就保持原序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42// 主要是找出四个节点:pre, left, right, post 然后反转[left, right],最后接上left.next和pre.next
public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode pre = dummy; // 反转左端点左侧
ListNode right = dummy; // 反转右端点
while(right.next != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < k && right != null; i++) {
right = right.next;
}
if(right == null) break;
ListNode left = pre.next; // 反转左端点
ListNode post = right.next; // 反转右端点右侧
right.next = null;
pre.next = reverse(left);
left.next = post;
pre = left;
right = pre;
}
return dummy.next;
}
// 反转单一链表
private ListNode reverse(ListNode node) {
ListNode pre = null;
ListNode cur = node;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = next;
}
return pre;
}
3 链表中倒数第k个
- 快慢指针:先让快指针前进k步,然后一起前进直到fast指针到null
4 合并链表
1 | class Solution { |
5 寻找链表公共节点
快慢指针:先让长的链表先走k步,然后一起走
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int lena = 0, lenb = 0;
ListNode a = headA, b = headB;
while(a != null){
lena++;
a = a.next;
}
while(b != null){
lenb++;
b = b.next;
}
int d = lena - lenb;
if(d > 0){
while(d-- > 0)
headA = headA.next;
}else if(d < 0){
d = -d;
while(d-- > 0)
headB = headB.next;
}
while(headA != headB){
headA = headA.next;
headB = headB.next;
}
return headA;
}
}循环指针:两个指针分别先走自己的链表,再走另一条链表,如果有公共节点,则会再某一时刻相同
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode A = headA, B = headB;
while (A != B) {
A = A != null ? A.next : headB;
B = B != null ? B.next : headA;
}
return A;
}
}
6 随机链表的复制
方式一:使用map:第一遍构造原node和新node的对应关系,第二遍构造原node的next和random指针和新node的next和random指针的关系
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
Map<Node, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
// 3. 复制各节点,并建立 “原节点 -> 新节点” 的 Map 映射
while(cur != null) {
map.put(cur, new Node(cur.val));
cur = cur.next;
}
cur = head;
// 4. 构建新链表的 next 和 random 指向
while(cur != null) {
map.get(cur).next = map.get(cur.next);
map.get(cur).random = map.get(cur.random);
cur = cur.next;
}
// 5. 返回新链表的头节点
return map.get(head);
}
}方式二:考虑构建 原节点 1 -> 新节点 1 -> 原节点 2 -> 新节点 2 -> …… 的拼接链表,如此便可在访问原节点的 random 指向节点的同时找到新对应新节点的 random 指向节点。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null) return null;
Node cur = head;
// 1. 复制各节点,并构建拼接链表
while(cur != null) {
Node tmp = new Node(cur.val);
tmp.next = cur.next;
cur.next = tmp;
cur = tmp.next;
}
// 2. 构建各新节点的 random 指向
cur = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.random != null)
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
cur = cur.next.next;
}
// 3. 拆分两链表
cur = head.next;
Node pre = head, res = head.next;
while(cur.next != null) {
pre.next = pre.next.next;
cur.next = cur.next.next;
pre = pre.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
pre.next = null; // 单独处理原链表尾节点
return res; // 返回新链表头节点
}
}
7 归并排序
- 给你链表的头结点
head,请将其按 升序 排列并返回 排序后的链表
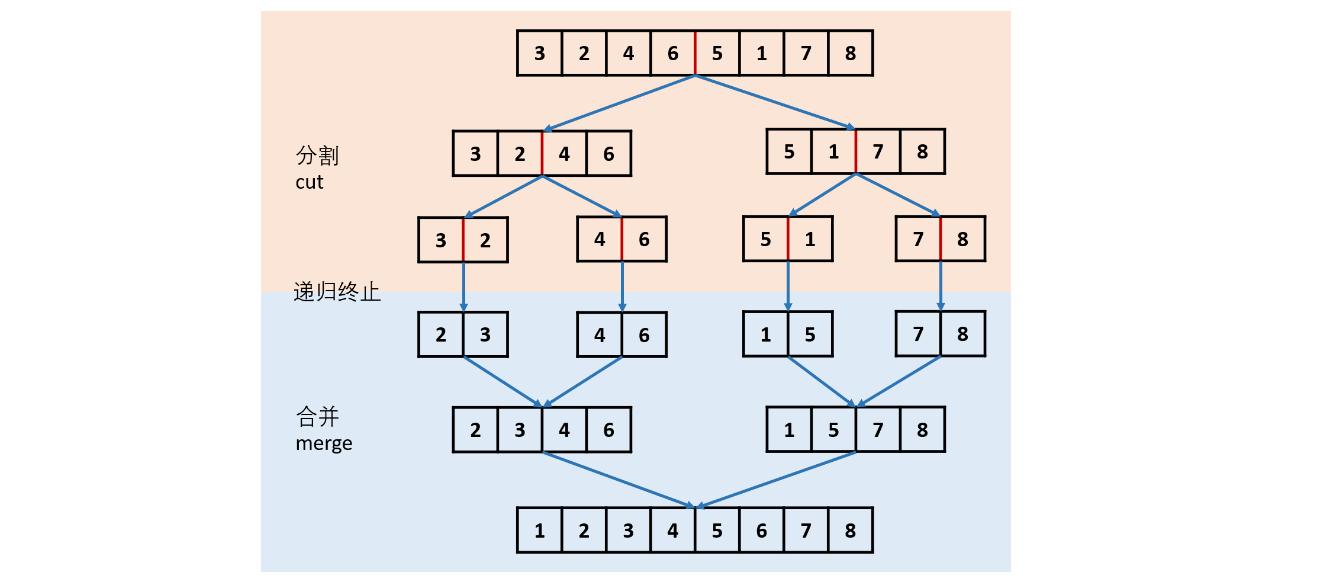
1 | public ListNode sortList(ListNode head) { |
8 合并k个升序链表
法1:优先级队列
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
PriorityQueue<ListNode> queue = new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<ListNode>() {
public int compare(ListNode node1, ListNode node2) {
return node1.val - node2.val;
}
});
for (ListNode node : lists) {
if (node != null) {
queue.offer(node);
}
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode cur = dummy;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
ListNode node = queue.poll();
cur.next = node;
cur = cur.next;
if (node.next != null) {
queue.offer(node.next);
}
}
return dummy.next;
}法2:分治合并
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45class Solution {
public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
}
private ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
return lists[l];
}
if (l > r) {
return null;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
// 分
return merge2Lists(merge(lists, l, mid), merge(lists, mid+1, r));
}
// 治
private ListNode merge2Lists(ListNode node1, ListNode node2) {
if (node1 == null || node2 == null) {
return node1 == null ? node2 : node1;
}
ListNode dummy = new ListNode();
ListNode cur = dummy;
ListNode node1Temp = node1;
ListNode node2Temp = node2;
while (node1Temp != null && node2Temp != null) {
if (node1Temp.val < node2Temp.val) {
cur.next = node1Temp;
node1Temp = node1Temp.next;
} else {
cur.next = node2Temp;
node2Temp = node2Temp.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = node1Temp == null ? node2Temp : node1Temp;
return dummy.next;
}
}
二 数组
双指针:前后夹击
滑动窗口:一前一后
和为k的子数组
方法一:前缀和+暴力O(n2)
方法二:前缀和+哈希表O(n)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19// key:前缀和,value:key 对应的前缀和的个数
Map<Integer, Integer> preSumFreq = new HashMap<>();
// 对于下标为 0 的元素,前缀和为 0,个数为 1
preSumFreq.put(0, 1);
int preSum = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
preSum += num;
// 先获得前缀和为 preSum - k 的个数,加到计数变量里
if (preSumFreq.containsKey(preSum - k)) {
count += preSumFreq.get(preSum - k);
}
// 然后维护 preSumFreq 的定义
preSumFreq.put(preSum, preSumFreq.getOrDefault(preSum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
寻找数组中的众数(一定存在)
哈希表
排序,然后中间的就是众数
Boyer-Moore 投票算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0) {
return -1;
}
int temp = nums[0];
int count = 1;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length - 1; i++) {
if(nums[i] == temp) {
count++;
}else {
count--;
if(count == 0) {
// 因为一定存在众数,所以count = 0时i一定不是最后一个
temp = nums[++i];
count++;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
2.1 股票问题
动态规划
只能买卖一次
dp[i]表示第i天所能获得的最大利润- 动态维护一个最小价格
minPrice dp[i] = max(dp[i-1], price[i] - minPrice)
可以多次买卖,同一时刻最多持有一股
dp[i][j],j表示状态0为没有股票,1表示持有股票,表示第i天的利润。dp[0][1] = -price[0]- 状态转移
dp[i][0] = max(dp[i-1][0], dp[i-1][1] + prices[i])维持前一天状态or当天卖掉dp[i][1] = max(dp[i-1][1], dp[i-1][0] - prices[i])维持前一天状态or当天买入
可以完成两次买卖,同一时刻最多持有一股
- 状态说明
- 未进行操作,利润为0,可以不记录
- 只买了一次 buy1
- 买一次和卖一次 sell1
- 买两次和卖一次 buy2
- 买两次和卖两次 sell2
- 初始状态
buy1 = buy2 = -prices[0]sell1= sell2 = 0
- 状态转移
buy1 = Math.max(buy1, -prices[i]);sell1 = Math.max(sell1, buy1 + prices[i]);buy2 = Math.max(buy2, sell1 - prices[i]);sell2 = Math.max(sell2, buy2 + prices[i]);
- 状态说明
可以完成k次买卖,同一时刻最多持有一股
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40public int maxProfit(int k, int[] prices) {
int n = prices.length;
// 1 定义
// buy[i][j] 第i天进行了j笔交易且还有股票的情况下的最大利润
// sell[i][j] 第i天进行了j笔交易且没有股票的情况下的最大利润
int[][] buy = new int[n][k+1];
int[][] sell = new int[n][k+1];
// 2 初始状态:初始化 第一行和第一列
// 2.1 只买一股但是不卖: buy[0:n-1][0] = -prices[0]
// 2.2 第1天最多操作一次:buy[0][1:k] 、sell[0][1:k]
buy[0][0] = -prices[0];
// buy[1:n-1][0] sell[1:n-1][0]
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
buy[i][0] = Math.max(buy[i-1][0], -prices[i]);
// sell[i][0] = 0;
}
// buy[0][1:k] sell[0][1:k]
for(int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
// 没有意义的数据:第一次不可能完成一次完整交易, /2是为了防止数据溢出
buy[0][j] = Integer.MIN_VALUE / 2;
sell[0][j] = Integer.MIN_VALUE / 2;
}
// 3 状态转移
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
for(int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
// 第i天持股且完成了j次交易:由i-1天持股状态变来 or i-1天不持股但是第i天买入
buy[i][j] = Math.max(buy[i-1][j], sell[i-1][j] - prices[i]);
// 第i天不持股完成了j次交易:由i-1天不持股状态变来 or i-1天持股但是第i天卖出
sell[i][j] = Math.max(sell[i-1][j], buy[i-1][j-1] + prices[i]);
}
}
// 4 返回sell[n-1]中最大的一个,分别对应完成了k次交易后的最大收益
return Arrays.stream(sell[n - 1]).max().getAsInt();
}
2.2 吃橘子(记忆存储dp)
厨房里总共有
n个橘子,你决定每一天选择如下方式之一吃这些橘子:- 吃1个
- 吃1/2 前提是
n被2整除 - 吃2/3 前提是
n被3整除
返回吃掉所有橘子最小的天数
法1:动态规划,
int[] dp = new int[n],时间复杂度O(n)法2:记忆存储,不一个一个的遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15Map<Integer, Integer> memo = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
public int minDays(int n) {
if(n <= 1) {
return n;
}
if(memo.containsKey(n)) {
return memo.get(n);
}
memo.put(n, Math.min(n % 2 + 1 + minDays(n / 2), n % 3 + 1 + minDays(n / 3)));
return memo.get(n);
}
2.3 矩阵中最大得分(二维前缀和)
给一个二维矩阵,求出其中的一个子矩阵(至少包含两个单元),使其
右下角-左上角的值最大二维前缀和+动态规划
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20public int maxScore(List<List<Integer>> grid) {
int ans = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int m = grid.size()
int n = grid.get(0).size();
// f[i+1][j+1]表示矩阵左上角[0,0],右下角[i,j]的子矩阵的最小值
// f[i+1][j+1] = min(f[i+1][j], f[i][j+1], grid[i][j])
int[][] f = new int[m + 1][n + 1];
Arrays.fill(f[0], Integer.MAX_VALUE);
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
f[i + 1][0] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
int mn = Math.min(f[i + 1][j], f[i][j + 1]); // 上面和左边拿小的那个
int x = grid.get(i).get(j);
ans = Math.max(ans, x - mn);
f[i + 1][j + 1] = Math.min(mn, x);
}
}
return ans;
}
2.4 数组合并问题
关键是先将数组的左端点或者右端点按照大小排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11Arrays.sort(points, new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] a, int[] b) {
// 按照数组右边界从小到大排序
return Integer.compare(a[1], b[1]);
}
});
// 这里有一个坑:不能 return a[1] - b[1],因为如果两个数组的左边界是Integer.MIN_VALUE,相减会导致超出int范围,返回错误的结果,Integer.compare的源码:
public static int compare(int x, int y) {
return x < y ? -1 : (x == y ? 0 : 1);
}
2.5 最大子数组
给你一个整数数组 nums ,请你找出一个具有最大和的连续子数组(子数组最少包含一个元素),返回其最大和。
法1:动态规划,O(n)时间
法2:分治,O(logn)
1 | class Solution { |
2.6 最大子数组Ⅱ
在2.5的基础上,添加一个可以首尾相连的条件(本质还是dp,但是很巧妙)
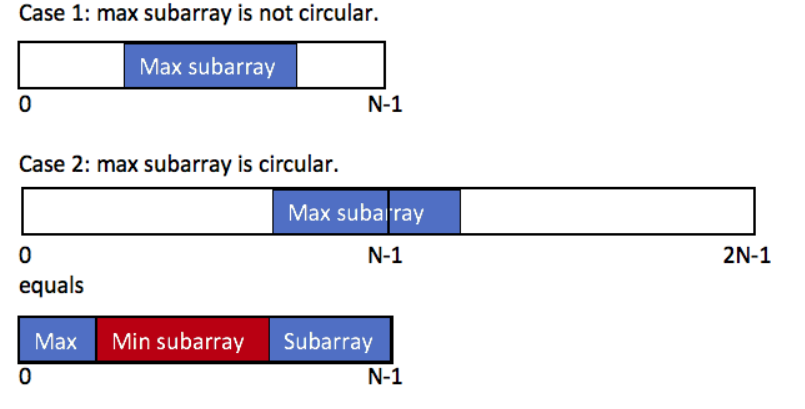
1 | public int maxSubarraySumCircular(int[] A) { |
2.7 二分查找
确定区间:左闭右闭 or 左闭右开
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13int l = 0;
int r = nums.length - 1;
while (l <= r) { // 左闭右闭
int mid = l + (r - l) / 2; // 注意越界问题
if (nums[mid] > target) {
r = mid - 1;
} else if (nums[mid] < target) {
l = mid + 1;
} else {
return mid;
}
}
return -1;
2.8 快速排序
时间O(NlogN),空间O(logN)~O(N),
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34private int[] fastSort(int[] nums, int l, int r) { // 升序
if (l >= r) {
return nums;
}
// int target = nums[l]; // 哨兵
int i = l;
int j = r;
while (i < j) {
while (i < j && nums[j] >= nums[l]) { // 哨兵在左,一定是从右边开始
j--;
}
while (i < j && nums[i] <= nums[l]) {
i++;
}
if (i < j) {
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
int temp = nums[l];
nums[l] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
fastSort(nums, l, j-1);
fastSort(nums, j+1, r);
return nums;
}
2.9 归并排序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27void mergeSort(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
// 终止条件
if (l >= r) {
return;
}
// 递归划分
int m = (l + r) / 2;
mergeSort(nums, l, m);
mergeSort(nums, m + 1, r);
// 合并子数组
int[] tmp = new int[r - l + 1]; // 暂存需合并区间元素
for (int k = l; k <= r; k++) {
tmp[k - l] = nums[k];
}
int i = 0, j = m - l + 1; // 两指针分别指向左/右子数组的首个元素
for (int k = l; k <= r; k++) { // 遍历合并左/右子数组
if (i == m - l + 1) {
nums[k] = tmp[j++];
} else if (j == r - l + 1 || tmp[i] <= tmp[j]) {
nums[k] = tmp[i++];
} else {
nums[k] = tmp[j++];
}
}
}
2.10
数组中前k个最频繁的数(
hashMap + PriorityQueue)O(NlogN)- 更好的方法:桶排序
O(N)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> frequencyMap = new HashMap<>();
// 统计每个数字出现的频率
for (int num : nums) {
frequencyMap.put(num, frequencyMap.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
// 创建桶,桶的索引是频率,值是具有相同频率的数字列表
List<Integer>[] buckets = new List[nums.length + 1]; // 比如1出现了3次,1就会在索引为3的桶出现
for (int key : frequencyMap.keySet()) {
int frequency = frequencyMap.get(key);
if (buckets[frequency] == null) {
buckets[frequency] = new ArrayList<>();
}
buckets[frequency].add(key);
}
// 从高频到低频遍历桶,收集前 k 个频率最高的元素
List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = buckets.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (buckets[i] == null) {
continue;
}
if (result.size() >= k) {
break;
}
int index = 0;
while (result.size() < k && index < buckets[i].size()) {
result.add(buckets[i].get(index++));
}
}
// 转换为数组返回
return result.stream().mapToInt(i -> i).toArray();
}- 更好的方法:桶排序
三 图
3.1 字典树
典型应用是用于统计,排序和保存大量的字符串(但不仅限于字符串)。本质就是一个Node对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45class Trie {
private Trie[] children;
private boolean isEnd;
public Trie() {
children = new Trie[26];
isEnd = false;
}
public void insert(String word) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < word.length(); i++) {
char ch = word.charAt(i);
int index = ch - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
node.children[index] = new Trie();
}
node = node.children[index];
}
node.isEnd = true;
}
public boolean search(String word) {
Trie node = searchPrefix(word);
return node != null && node.isEnd;
}
public boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
return searchPrefix(prefix) != null;
}
private Trie searchPrefix(String prefix) {
Trie node = this;
for (int i = 0; i < prefix.length(); i++) {
char ch = prefix.charAt(i);
int index = ch - 'a';
if (node.children[index] == null) {
return null;
}
node = node.children[index];
}
return node;
}
}
四 位运算
1 | n >> 1; // 向右移动一位 100110 ==> 010011,相当于/2 |
4.1 快速幂
快速幂法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17static long qpow(int a, int b, int mod) {
// 求a翻倍b次,结果取模mod
long res = 1, t = a;
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) { // 只计算末尾是1的指数,因为任何数的0次方=1,就没必要乘了
res = (res * t) % mod;
}
b >>= 1; // 指数位右移动:1011(2) -> 101(2)
t = (t * t) % mod;
}
return res;
}
// 调用
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
res = (res + qpow(2, s[i + 1], mod) * a[i] % mod) % mod;
}
五 其他
5.1 判断是否为质数
只要把循环一直从2尝试到根号x(一个数的两个因数中,毕然有一个小于等于根号x,一个大于等于根号x)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11public static boolean isPrime1(int x){
if(x <= 2) {
return true;
}
for(int i = 2; i <= Math.sqrt(x); i++){
if(x % j==0){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}

